Due to its potential to democratize software development, low-code is the biggest trend in modern business tech and it is growing fast. With its formidable array of low/no-code tools – Power Apps, Power Automate, Power BI, and Power Virtual Agents – Microsoft’s Power Platform offers organizations amazing possibilities for rapid app development without traditional coding.
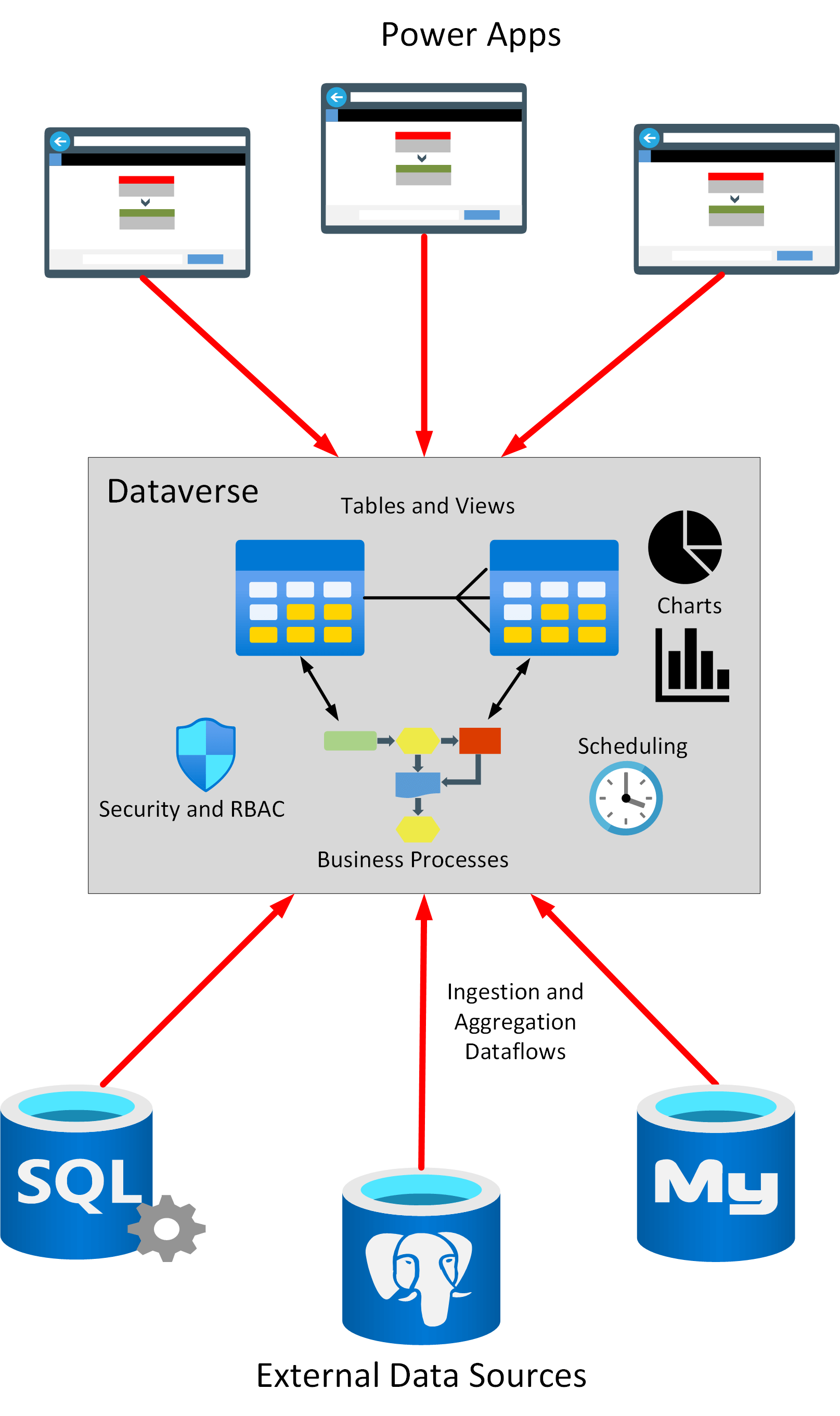
Now, with the unveiling of Microsoft Dataverse, organizations not only enjoy the frontend tools they need to create custom low-code solutions, they also obtain the backend infrastructure they need to access, integrate, store, and maintain the data that powers their applications.
Before now, SharePoint was the go-to for storage and integration of business application data. Today, Dataverse presents a powerful low-code alternative that organizations and their teams can learn to use with little to no coding skill.